Why do we need more fibre in our diet? Did...
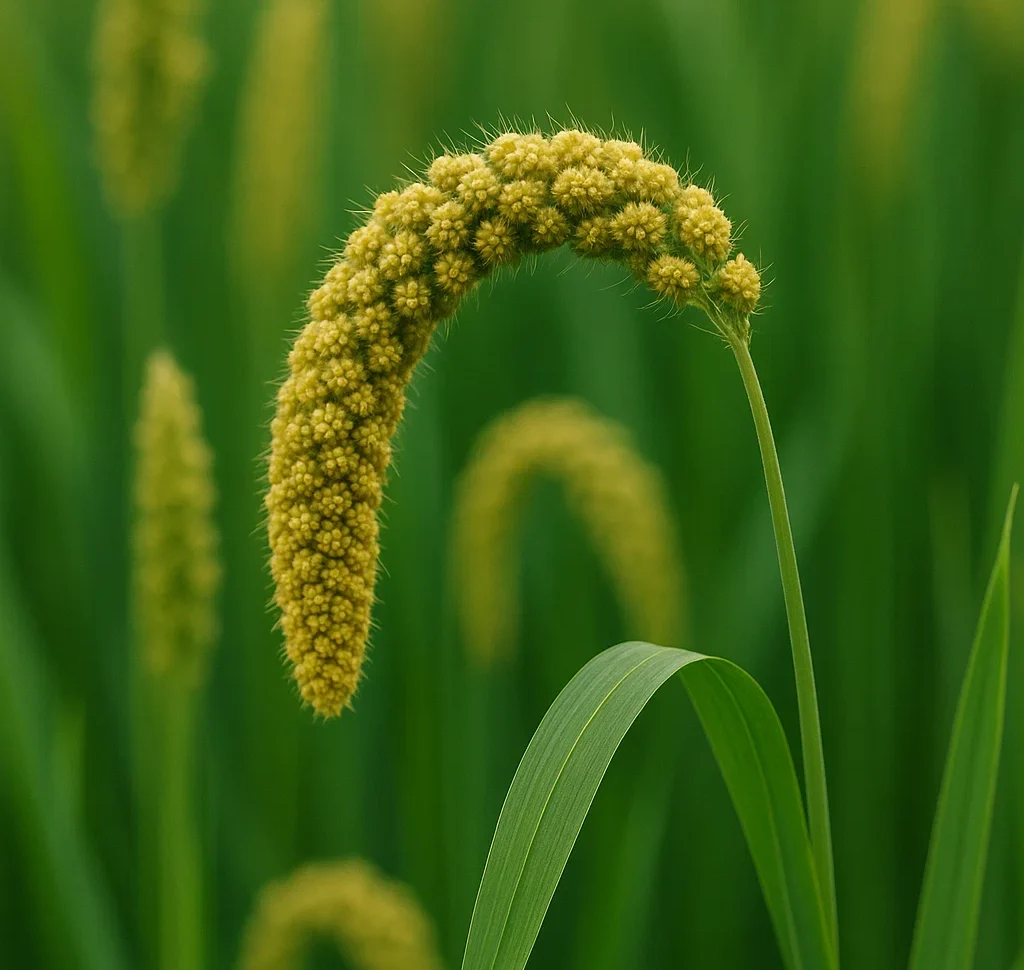
Read MoreFoxtail Millet (Setaria italica) has been overshadowed by its more glamorous cereal cousins, this resilient and nutritious grain is experiencing a well-deserved resurgence. In this blog, we will discuss on the fascinating history of foxtail millet, explore its remarkable health benefits, uncover its diverse culinary uses, explore where it thrives, and look at its promising future as an environmentally friendly crop at the time of the climate change crisis.
Millets are deeply connected with the history of human civilization on this earth. Foxtail millet originating in China around 8,000 years ago, it stands as one of the earliest domesticated crops. Archaeological evidence from sites like Cishan and Jiahu in northern China reveals the significant role this little grain has played in the diets of Neolithic communities. Its adaptability and short growing season likely contributed to its early adoption and widespread cultivation.
From its Chinese heartland, foxtail millet gradually spread across Asia, reaching India, Japan, Korea, and eventually making its way to Europe and Africa. Ancient texts and historical records from these regions validates its importance as a staple part of our food. diet. In India, it’s known by various names like kangni or korra and holds cultural significance in traditional diets. Similarly, in Italy, it was cultivated in ancient times and known as panico. This long and rich history underscores the inherent value and resilience of foxtail millet as a reliable food source.
Foxtail Millet’s Nutritional Benefits!
Beyond the historical significance, foxtail millet boasts an impressive nutritional profile, making it a valuable addition to a modern, health-conscious diet. It is naturally gluten-free, making it an excellent choice for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Some of the nutritional benefits of foxtail millet are:
- Rich in Dietary Fiber: Foxtail millet is packed with both soluble and insoluble fiber. This high fiber content aids in digestion, promotes gut health, helps regulate blood sugar levels, and contributes to feelings of fullness, potentially assisting in weight management. Note: to get the max fiber content, millet in general needs to be soaked for 6 hours prior to cooking according to historical sources.
- Good Source of Minerals: It provides essential minerals like iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium. Iron is crucial for oxygen transport, magnesium plays an important role in muscle and nerve function, phosphorus is important for bone health, and potassium helps regulate blood pressure.
- Antioxidant Properties: Foxtail millet contains various antioxidants, including phenolic compounds and flavonoids. These compounds help combat oxidative stress in the body, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases according to www.acsnutritionaltherapist.co.uk (Source)
- Source of Protein: While not as high in protein as some other grains, foxtail millet contributes a decent amount of plant-based protein to the diet, essential for building and repairing tissues.
- Low Glycemic Index: Compared to refined grains, foxtail millet has a lower glycemic index, meaning it causes a slower and steadier rise in blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for individuals managing diabetes or seeking stable energy levels.
Regular consumption of foxtail millet can contribute to improved heart health, better blood sugar control, enhanced digestion, and a boost in overall well-being.
Culinary Versatility: Various Uses of Foxtail Millet
Mild and slightly nutty flavor of foxtail millet makes it incredibly versatile in the kitchen. It can be incorporated into a wide array of dishes, both sweet and savory, across different cuisines.
Some of the popular ways to use foxtail millet as part of our food diet:
- As a Gluten-Free Grain: Soaked and Cooked whole, it can serve as a nutritious alternative to rice, quinoa, or couscous. It can be cooked well with vegetables, lentils, beans, and various sauces.
- Ground into Flour: Foxtail millet flour can be used to make gluten-free breads, rotis, pancakes, dosas, and other baked goods. It lends a slightly sweet and nutty flavor to the final product.
- In Porridges and Breakfast Bowls: Cooked with milk or water, it makes a creamy and satisfying porridge, perfect for a healthy breakfast. Fruits, nuts, and sweeteners can be added for extra flavor and nutrition.
- In Salads and Pilafs: Cooked millet adds texture and substance to salads and pilafs, absorbing flavors beautifully from dressings and spices.
- As Animal Feed: Beyond human consumption, foxtail millet is also a valuable source of fodder for livestock.
From traditional ethinic Indian dishes like upma and khichdi to innovative gluten-free baking, the culinary possibilities of foxtail millet are vast and can be explored further with imagination.
Global Cultivation of Foxtail Millet
Foxtail millet is known for its adaptability to diverse agro-climatic conditions, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. This resilience has made it a crucial crop in many parts of the world.
Key regions where foxtail millet is currently grown include:
- Asia: China and India remain the largest producers globally. It is also cultivated in Southeast Asian countries like Indonesia and Thailand, as well as in Japan and Korea.
- Africa: Several African countries, particularly in East and West Africa, grow foxtail millet as a vital food source in drier areas.
- Europe: While its cultivation has declined compared to ancient times, some European countries still grow small quantities of foxtail millet.
- North and South America: Interest in foxtail millet is growing in these regions, particularly as a gluten-free alternative and a sustainable crop.
Its ability to thrive in less fertile soils and with lower water requirements compared to other major cereals makes it an important crop for food security in marginal environments.
Foxtail Millet and Environmental Sustainability
Increasing concerns about climate change and environmental degradation, foxtail millet stands out as an environmentally friendly crop with significant potential for sustainable agriculture.
- Drought Tolerance: Its inherent ability to withstand dry conditions makes it a resilient crop in water-scarce regions, reducing the reliance on extensive irrigation.
- Low Water Requirement: Compared to water-intensive crops like rice and wheat, foxtail millet requires significantly less water for cultivation.
- Short Growing Cycle: Its relatively short growing season allows for multiple cropping cycles in a year, potentially increasing overall productivity and land use efficiency.
- Adaptability to soils with less fertility: Foxtail millet can grow in less fertile soils, reducing the need for excessive synthetic fertilizers, which can have negative environmental impacts.
- Pest and Disease Resistance: It exhibits a natural resistance to certain pests and diseases, minimizing the need for chemical pesticides.
- Carbon Sequestration: Like other plants, foxtail millet absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, contributing to carbon sequestration in the soil.
Above characteristics positions foxtail millet as a valuable component of sustainable farming systems, promoting biodiversity, conserving water resources, and reducing the environmental footprint of agriculture.
Voices from the Field and Beyond: What Others Say About Foxtail Millet
The growing recognition of foxtail millet’s potential is reflected in the increasing attention it receives from researchers, farmers, and food advocates.
- Agricultural Scientists: Highlight its resilience, adaptability, and nutritional value, emphasizing its role in climate-smart agriculture and food security, particularly in vulnerable regions.
- Nutritionists and Health Experts: its gluten-free nature, high fiber content, and rich mineral profile, advocating for its inclusion in healthy and balanced diets.
- Farmers: In regions where it has been traditionally grown, farmers appreciate its low input requirements and reliable yields, contributing to their livelihoods. Emerging interest in other regions is driven by its sustainability and market potential.
- Food lovers and Chefs: They are increasingly experimenting with foxtail millet in innovative recipes, showcasing its versatility and appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking gluten-free options. Give us comments for Foxtail Millets innovative cooking ideas.
However, challenges remain in mainstreaming foxtail millet, including limited awareness among consumers, lack of processing infrastructure in some regions, and the need for further research to optimize its cultivation and utilization.
Foxtail Millet – What is the future?
The future of foxtail millet appears to be bright. As the world grapples with the challenges of feeding a growing population sustainably and addressing the impacts of climate change, this ancient grain truly offers a compelling solution.
Increased awareness of its nutritional benefits and environmental advantages is driving renewed interest among consumers and producers alike. Research and development efforts are focusing on improving varieties, developing efficient processing techniques, and exploring new applications in food and other industries.
Government initiatives and agricultural policies in some regions are beginning to recognize the importance of millets, including foxtail millet, in promoting dietary diversity and sustainable agriculture. The rising demand for gluten-free and plant-based foods further fuels its potential in modern markets.
Foxtail millet is more than just a forgotten grain from the past. It is a resilient, nutritious, and environmentally friendly crop with a rich history and a promising future. As we strive for healthier diets and more sustainable food systems, this golden grain is poised to play an increasingly significant role in nourishing both people and the planet. Embracing the versatility and value of foxtail millet can contribute to a more food-secure and environmentally conscious world.
Your Guts Are Your Second Brain: How Millet Impacts Your Gut Health
Understanding Your Second Brain Have you ever experienced butterflies in...
Read MoreFarm to Food: The Gluten Free Baking Revolution featuring Millets
The Ancient Grain Making Modern Waves Millets represent more than...
Read MoreIs Sorghum (Jowar) Gluten Free? Exploring guide for Celiac Disease, Gluten Free and Healthy Living
If you have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, finding safe...
Read More