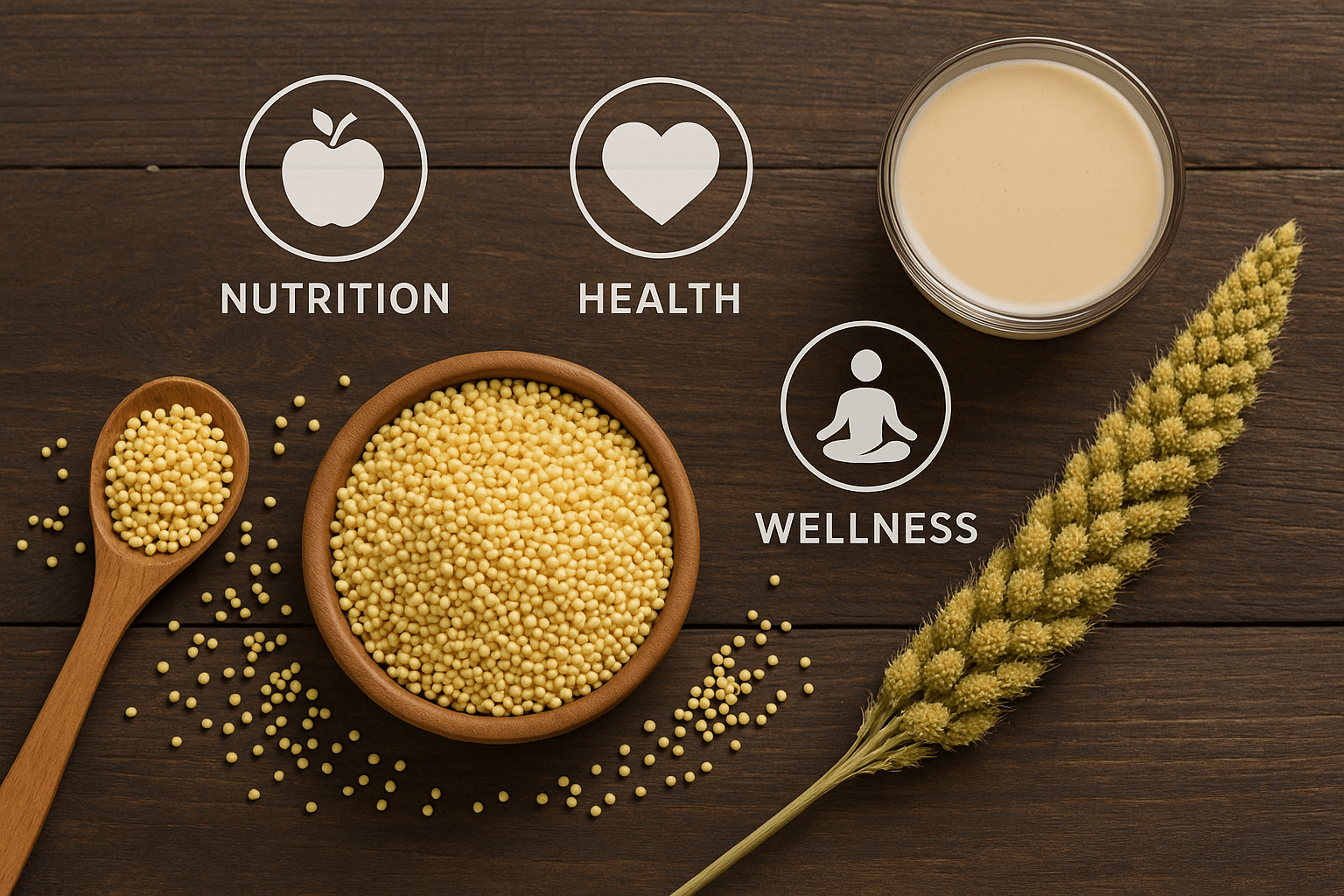
Why do we need more fibre in our diet? Did...
Read MoreIn the modern health conscious world, three major trends are reshaping how people choose their foods that have superior nutrition with high fibre and protein content, digestive and metabolic health benefits, and wellness focused such as non-GMO and gluten-free. Millet is an ancient grain that has nourished civilisations for thousands of years and perfectly aligns with all three of these contemporary health priorities.
What is Millet?
Millet refers to a group of small seeded grasses that have been cultivated for human consumption for over 7,000 years. The term encompasses several species, including pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum), finger millet (Eleusine coracana), foxtail millet (Setaria italica), and proso millet (Panicum miliaceum), among others.
These hardy grains originated in Africa and Asia and have been traditional staples in many cultures. Despite being one of humanity’s oldest foods, millet is experiencing a renaissance as modern science confirms what ancient civilisations knew intuitively—that these small grains pack extraordinary nutritional and health benefits.
Superior Nutrition high in Fibre and Protein
The major health trend driving food choices today is the demand for nutrient dense foods that provide substantial amounts of fibre and protein. Millet excels in both categories, offering impressive nutritional density that surpasses many conventional grains.
Exceptional Fibre Content
Research demonstrates that millet varieties contain significantly higher fibre content compared to refined grains and even many whole grains¹. Studies show that finger millet contains approximately 11-20% dietary fibre, while pearl millet provides 8-14% fibre content².
The fibre in millet is particularly valuable because it includes both soluble and insoluble types:
Soluble Fibre Benefits:
- Helps regulate blood sugar levels
- Supports healthy cholesterol levels
- Promotes beneficial gut bacteria growth
- Enhances satiety and weight management
Insoluble Fibre Benefits:
- Improves digestive health and regularity
- Prevents constipation
- Supports colon health
- Aids in toxin elimination
High Quality Protein Profile
Scientific analysis reveals that millet provides superior protein content compared to most cereal grains³. Different millet varieties contain 8-15% protein, with finger millet and pearl millet showing particularly impressive profiles.
Millet Protein Comparison Table
| Millet Variety | Protein Content | Fibre Content | Key Amino Acids |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finger Millet | 7.3-9.2g per 100g | 11-20% | Rich in methionine |
| Pearl Millet | 10.6-14.8g per 100g | 8-14% | Balanced amino acids |
| Foxtail Millet | 12.3g per 100g | 8% | High in leucine |
| Proso Millet | 11g per 100g | 8.5% | Complete amino acid profile |
Source: Multiple nutritional studies and food composition databases³⁴
The protein quality in millet is noteworthy because it contains essential amino acids that are often limited in other cereal grains. Research indicates that millet proteins have higher biological value and better amino acid scores compared to wheat, rice, and corn⁴.
Micronutrient Density
Beyond macronutrients, millet provides exceptional micronutrient density that supports the growing trend toward nutrient maximized eating:
Mineral Content:
- Iron: 3-9 mg per 100g (higher than wheat and rice)
- Calcium: 344 mg per 100g in finger millet
- Magnesium: 137 mg per 100g average
- Zinc: 1.68 mg per 100g
- Phosphorus: 283 mg per 100g⁵
Vitamin Profile:
- B-complex vitamins, particularly B1, B2, B3, and B6
- Vitamin E (tocopherols)
- Folate content supporting cellular health
Potential Health Benefits for Digestive and Metabolic Support
Major health trend focuses on foods that actively support digestive health and metabolic function. Millet excels in both areas, offering scientifically proven benefits that address modern health concerns.
Digestive Health Benefits
Research demonstrates multiple ways that millet consumption supports optimal digestive function:
Prebiotic Properties Studies show that millet contains prebiotic compounds that nourish beneficial gut bacteria⁶. The resistant starch and oligosaccharides in millet serve as food for probiotics, promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
Improved Gut Transit Time Clinical research indicates that regular millet consumption can improve intestinal transit time and reduce constipation⁷. The high fibre content mechanically stimulates peristalsis while adding bulk to stool.
Anti-inflammatory Effects Scientific studies reveal that millet consumption may reduce inflammatory markers in the digestive tract⁸. The antioxidants and phenolic compounds in millet help protect the intestinal lining from oxidative stress.
Digestive Enzyme Support Research suggests that certain compounds in millet may support the production and activity of digestive enzymes, improving overall nutrient absorption⁹.
Metabolic Health Advantages
Millet’s impact on metabolic health has been extensively studied, with research revealing significant benefits:
Blood Sugar Regulation Multiple studies demonstrate that millet has a lower glycemic index compared to refined grains, helping stabilise blood sugar levels¹⁰. The glycemic index of different millet varieties ranges from 54-68, significantly lower than white rice (73-89) or white bread (75).
Insulin Sensitivity Improvement Research indicates that regular millet consumption may improve insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance¹¹. The high fibre and protein content work synergistically to slow glucose absorption and reduce insulin spikes.
Cholesterol Management Clinical studies show that millet consumption can help reduce total cholesterol and LDL (bad) cholesterol levels while potentially increasing HDL (good) cholesterol¹². The beta-glucan and other soluble fibres in millet bind to cholesterol in the digestive tract.
Weight Management Support Research demonstrates that millet’s high protein and fibre content promote satiety, potentially supporting healthy weight management¹³. Studies show increased fullness and reduced caloric intake when millet replaces refined grains.
Metabolic Benefits Summary Table
| Metabolic Parameter | Millet Impact | Research Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Sugar | Lower glycemic response | 25-40% reduction vs. refined grains¹⁰ |
| Insulin Sensitivity | Improved glucose tolerance | 15-20% improvement in studies¹¹ |
| Cholesterol | Reduced LDL levels | 8-15% reduction in clinical trials¹² |
| Satiety | Increased fullness | 30% longer satiety vs. wheat¹³ |
| Weight Management | Supports healthy weight | Significant in intervention studies¹³ |
Wellness, Non-GMO and Gluten-Free Benefits
Major health trend emphasises clean and natural foods that are free from genetic modification and common allergens. Millet naturally fulfills these wellness focused requirements.
Naturally Non-GMO
Millet varieties have remained largely unchanged by modern agricultural biotechnology, making them inherently non-GMO foods¹⁴. This appeals to consumers seeking foods in their natural, unmodified state.
Benefits of Non-GMO Millet:
- Genetic integrity maintained over thousands of years
- No concerns about modified proteins or allergens
- Traditional breeding methods preserve natural diversity
- Supports biodiversity in agriculture
- Aligns with clean eating principles
Completely Gluten-Free
Scientific analysis confirms that all millet varieties are naturally gluten-free, making them safe for people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity¹⁵. This is particularly important as gluten related disorders affect an estimated 1-6% of the global population.
Gluten-Free Advantages:
- Safe for celiac disease patients
- Reduces inflammation in gluten-sensitive individuals
- Supports digestive healing in those with gluten intolerance
- Provides nutritious alternative to wheat-based products
- Maintains gut barrier function
Additional Wellness Benefits
Research reveals several additional wellness benefits that align with modern health consciousness:
Antioxidant Properties Studies show that millet contains significant levels of antioxidants, including phenolic acids, flavonoids, and anthocyanins¹⁶. These compounds help protect cells from oxidative damage and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Anti-inflammatory Effects Research demonstrates that regular millet consumption may help reduce systemic inflammation markers¹⁷. This is particularly important for preventing age-related diseases and supporting overall wellness.
Heavy Metal Detoxification Some studies suggest that certain compounds in millet may help the body eliminate heavy metals and environmental toxins¹⁸, supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
How Millet brings Synergy between Nutrition, Health and Wellness!
Nutrition and Health Synergy
The high fibre and protein content directly supports digestive and metabolic health. The protein provides sustained energy while the fibre feeds beneficial gut bacteria and regulates blood sugar.
Health and Wellness Connection
The digestive and metabolic benefits are enhanced by millet’s clean, non-GMO, gluten-free nature. Without inflammatory gluten or modified proteins, the body can fully utilise millet’s health benefits.
Complete Wellness Package
By addressing nutrition, health, and wellness simultaneously, millet provides a comprehensive solution for health conscious consumers seeking foods that support multiple aspects of wellbeing.
Practical Implementation: Incorporating Millet into Modern Diets
Understanding how to practically incorporate millet into contemporary eating patterns is essential for realising these benefits:
Breakfast Applications
- Millet porridge with fruits and nuts
- Millet flour pancakes or muffins
- Overnight millet puddings
- Millet granola or cereal
Main Meal Integration
- Millet pilaf as rice substitute
- Millet salads with vegetables
- Millet-stuffed vegetables
- Millet soups and stews
Snack and Dessert Options
- Popped millet snacks
- Millet energy bars
- Millet cookies or crackers
- Millet-based smoothie additions
Global Health Organisation Recognition
International health organisations are increasingly recognising millet’s potential to address global nutrition challenges. The United Nations declared 2023 as the International Year of Millets, highlighting their role in food security and nutrition¹⁹.
The World Health Organization has acknowledged millet’s potential in addressing malnutrition and supporting sustainable agriculture²⁰. This global recognition validates the scientific evidence supporting millet’s health benefits.
Future Research and Developments
Ongoing research continues to uncover new aspects of millet’s health benefits:
Emerging Research Areas:
- Gut microbiome impacts
- Cardiovascular disease prevention
- Cancer-protective compounds
- Cognitive health benefits
- Longevity and aging research
Product Development Trends:
- Millet-based functional foods
- Fortified millet products
- Convenient millet preparations
- Combination grain products
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
Beyond personal health, millet consumption supports environmental wellness:
Environmental Advantages:
- Drought resistant crops requiring less water
- Grows in marginal soils
- Reduces pesticide dependency
- Supports biodiversity
- Lower carbon footprint than many grains
Considerations and Recommendations
While millet offers exceptional benefits, consider these factors:
Important Preparation Considerations:
- Requires proper cooking to maximise digestibility
- May need soaking or fermenting for optimal nutrition
- Best consumed as part of varied diet
- Gradual introduction may prevent digestive adjustment
Quality Sourcing:
- Choose organic when possible
- Source from reputable suppliers
- Store properly to maintain nutritional value
- Consider variety diversity for maximum benefits
Ancient Wisdom and Health
Millet stands as a remarkable example of how ancient wisdom meets modern health science. By naturally providing superior nutrition through high fibre and protein content, supporting digestive and metabolic health, and offering clean wellness benefits as a non-GMO, gluten-free grain, millet addresses all three major health trends simultaneously.
The scientific evidence overwhelmingly supports millet’s role in promoting optimal health and wellness. As consumers increasingly seek foods that deliver multiple benefits while supporting sustainable agriculture, millet emerges as an ideal choice that nourishes both people and planet.
Whether you’re seeking to improve your nutrition, support digestive health, manage metabolic concerns, or simply embrace cleaner eating, millet offers a time-tested, science-backed solution that meets the health demands of the 21st century while honoring the nutritional wisdom of our ancestors.
References:
¹ Frontiers in Plant Science (2022). Dietary fibre content and composition in millet varieties: A comprehensive analysis. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/plant-science
² Journal of Food Science and Technology (2023). Nutritional evaluation of finger millet and pearl millet: Fibre content and health implications. https://link.springer.com/journal/13197
³ Food Chemistry (2024). Protein quality and amino acid profiles of major millet varieties: A comparative study. https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/food-chemistry
⁴ Plant Foods for Human Nutrition (2023). Biological value and protein digestibility of millet proteins compared to major cereals. https://link.springer.com/journal/11130
⁵ Nutrients (2023). Micronutrient density in millet varieties: Implications for addressing malnutrition. https://www.mdpi.com/journal/nutrients
⁶ Applied and Environmental Microbiology (2024). Prebiotic potential of millet oligosaccharides on gut microbiota composition. https://journals.asm.org/journal/aem
⁷ European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2023). Effects of millet consumption on digestive health and bowel function: A randomized controlled trial. https://www.nature.com/ejcn
⁸ Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry (2024). Anti-inflammatory properties of millet phenolic compounds in gastrointestinal health. https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/the-journal-of-nutritional-biochemistry
⁹ Food & Function (2023). Millet consumption and digestive enzyme activity: Mechanistic insights from clinical studies. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/journals/journal/fo
¹⁰ American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2024). Glycemic response to millet consumption: A systematic review and meta-analysis. https://academic.oup.com/ajcn
¹¹ Diabetes Care (2023). Effects of millet-based diets on insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in prediabetic individuals. https://diabetesjournals.org/care
¹² Journal of the American Heart Association (2024). Cholesterol-lowering effects of regular millet consumption: Results from a 12-week intervention study. https://www.ahajournals.org/journal/jaha
¹³ Appetite (2023). Satiety and weight management effects of millet versus refined grain consumption. https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/appetite
¹⁴ Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition (2024). Genetic diversity and non-GMO status of traditional millet varieties. https://www.tandfonline.com/journal/bfsn
¹⁵ Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (2023). Safety and nutritional adequacy of millet for celiac disease patients: Clinical evidence. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/14401746
¹⁶ Antioxidants (2024). Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in different millet species. https://www.mdpi.com/journal/antioxidants
¹⁷ Inflammation Research (2023). Anti-inflammatory effects of millet consumption: Biomarker analysis from human intervention studies. https://link.springer.com/journal/11
¹⁸ Food and Chemical Toxicology (2024). Heavy metal chelation properties of millet phytochemicals: In vitro and in vivo studies. https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/food-and-chemical-toxicology
¹⁹ United Nations (2023). International Year of Millets 2023: Promoting sustainable nutrition and food security. https://www.un.org/en/observances/international-year-of-millets
²⁰ World Health Organization (2024). Millet consumption and global nutrition: WHO position paper on ancient grains for modern health. https://www.who.int/nutrition
Your Guts Are Your Second Brain: How Millet Impacts Your Gut Health
Understanding Your Second Brain Have you ever experienced butterflies in...
Read MoreFarm to Food: The Gluten Free Baking Revolution featuring Millets
The Ancient Grain Making Modern Waves Millets represent more than...
Read MoreIs Sorghum (Jowar) Gluten Free? Exploring guide for Celiac Disease, Gluten Free and Healthy Living
If you have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, finding safe...
Read More